
Beware! Malware Targeting Endpoints on the Rise Ahead
All you need to do is listen to the news and you know that the cyber threat landscape in 2016 has gotten much worse. But what types of threats are driving companies to take action? And what actions are they taking?
To answer these questions, and more, we turned to SANS Institute, the leading organization for cybersecurity research, training and certification to conduct an in-depth survey of more than 300 enterprise customers across the globe. The survey, known as the 2016 SANS Threat Landscape Survey, explores the current state of the threat landscape and how these security threats are impacting organizations. In particular, it examines the types and the nature of threats attacking today’s organizations, and how these attacks are getting in.
Based on the survey results, the majority of threats coming into organizations over the last year used endpoints as their main point of entry, including PCs, laptops and tablets. And what types of threats were on the rise and targeting end-user systems? Twenty-seven percent of respondents identified phishing as the leading cause of significant incidents, followed by ransomware at 19% and spearphishing/whaling at 13%. Trojans, ransomware and spyware rounded out the list of top threats launched against organizations represented in this survey.
Phishing, ransomware and spearphishing/whaling also represented the fastest rising threat types. These threats are of particular concern because they often result in direct damages, through credential theft or the need to pay ransom to recover lost data (See Figure 1).
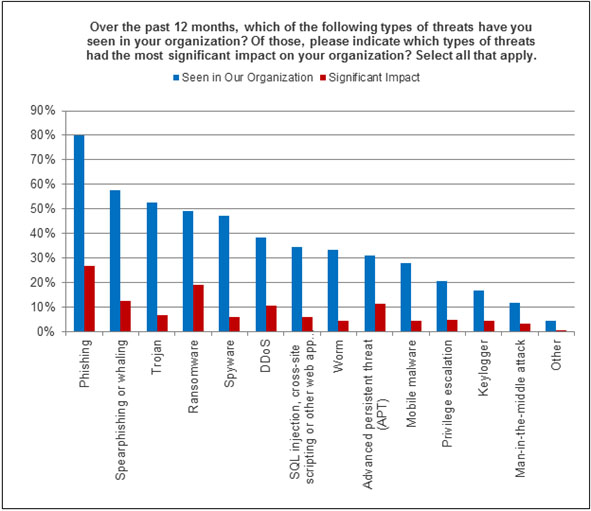
Figure 1. Attacks on the rise over the past 12 months, based on results from the 2016 SANS Threat Landscape Survey
What can organizations do to protect themselves from these types of attacks? Following the below few best practices can certainly help reduce the chances that an attack will enter your endpoints or network:
- Educate Your Employees – First and foremost, it’s important to make sure that your employees are educated about what to watch out for. This includes making sure the sender, attachments and URLs within emails are legitimate and trustworthy, as well as being watchful for unsettling content, for example an email stating that your bank account has been hacked. Keeping your employees aware and paying attention to what comes in their inbox is critical to preventing phishing, ransomware and other attacks from compromising your network.
- Think Beyond Signature-Based Protections – Traditional signature-based protections like antivirus are necessary, but are no longer sufficient. In recent years, cybercriminals have learned how to bypass traditional signature-based detection solutions, bringing in new technologies and tools that make it much harder for users to decipher if an email, website, a file, or a URL is truly legitimate or not. Hackers can also easily modify a variant of a particular malware, creating a brand new malware capable of avoiding detection by signature-based solutions. For these reasons, it has become essential for organizations today to employ multiple layers of protection, being sure to utilize solutions that can secure them from new, unknown malware and other sophisticated attacks for which there might not be available signatures.
Want to learn specific tips about how to protect your organization from ransomware and phishing attacks? Read our recent blogs 5 Tips to Fight Back Against Ransomware and 6 Tips to Outsmart the Phishermen.
At Check Point, we protect our customers from targeted endpoint attacks with Check Point SandBlast Agent. SandBlast Agent is a progressive solution that extends advanced threat prevention to end-user systems to defend against the full scope of zero-day threats and targeted attacks, including those using social engineering techniques. It is comprised of industry-leading technologies, such as:
- Threat Emulation (sandboxing): Advanced sandbox engine with patented CPU-level detection and the highest malware catch rate that quickly inspects files in a virtual sandbox.
- Threat Extraction: Reconstructs downloaded files in seconds, eliminating potential threats and promptly delivers a safe version to users.
- Zero Phishing™: Uses dynamic analysis and advanced heuristics to identify and prevent access to new and unknown phishing sites targeting user credentials through web browsers.
If you would like to learn more about the full results from the SANS 2016 Threat Landscape Survey, we invite you to read the whitepaper and view the replay of our webinar featuring Lee Neely, SANS Mentor Instructor here.









