Zero Trust Security in Action: Meet the New Check Point CloudGuard
It’s no surprise that compromised or stolen credentials are the leading attack vectors year to year. Overly permissive user and service accounts are created in a rush due to the agile development process – only to be abandoned after a few uses, leaving them vulnerable to hackers. This focus on velocity makes it increasingly difficult for organizations to know who has access to what data, and across which platforms.
According to Gartner, 75% of security failures will result from inadequate management of identities this year.
Many security professionals are concerned about the ease of overprovisioning and effectively managing access to reduce risks. To tackle this concern, organizations require tools that empower them to remain efficient while minimizing risk. The implementation of Zero Trust helps organizations reduce their risk and defend against credential-based attacks.
The Zero Trust model was established by Forrester in 2011 and provides a guiding principle of never trust, always verify. As organizations move to the cloud, shifting from perimeter protection to identity protection by adopting Zero Trust is essential to maintaining a high level of security. In traditional security models, there is an implicit level of trust placed in every user, device, and network within an organization’s network. However, this assumption of trust can leave organizations vulnerable to attacks.
According to the 2023 Cloud Security Report, respondents surveyed revealed that 35% of breaches that they experienced were caused by misconfigured assets or compromised accounts.
Many enterprises have adopted CloudGuard as a central component of their Zero Trust security strategy. Zero Trust promotes the principle of least privilege, which means users and systems only have access to the minimum resources necessary to perform their tasks. With CloudGuard’s Cloud Identity and Entitlement Management (CIEM), over-privileged entities are automatically detected, least-privileged recommendations are provided, and alerts are issued for anomalies in user permission usage and deviations from best practices.
But the work doesn’t stop there. To continue reducing the attack surface and limiting potential damage, Zero Trust can be implemented as a part of shifting security left.
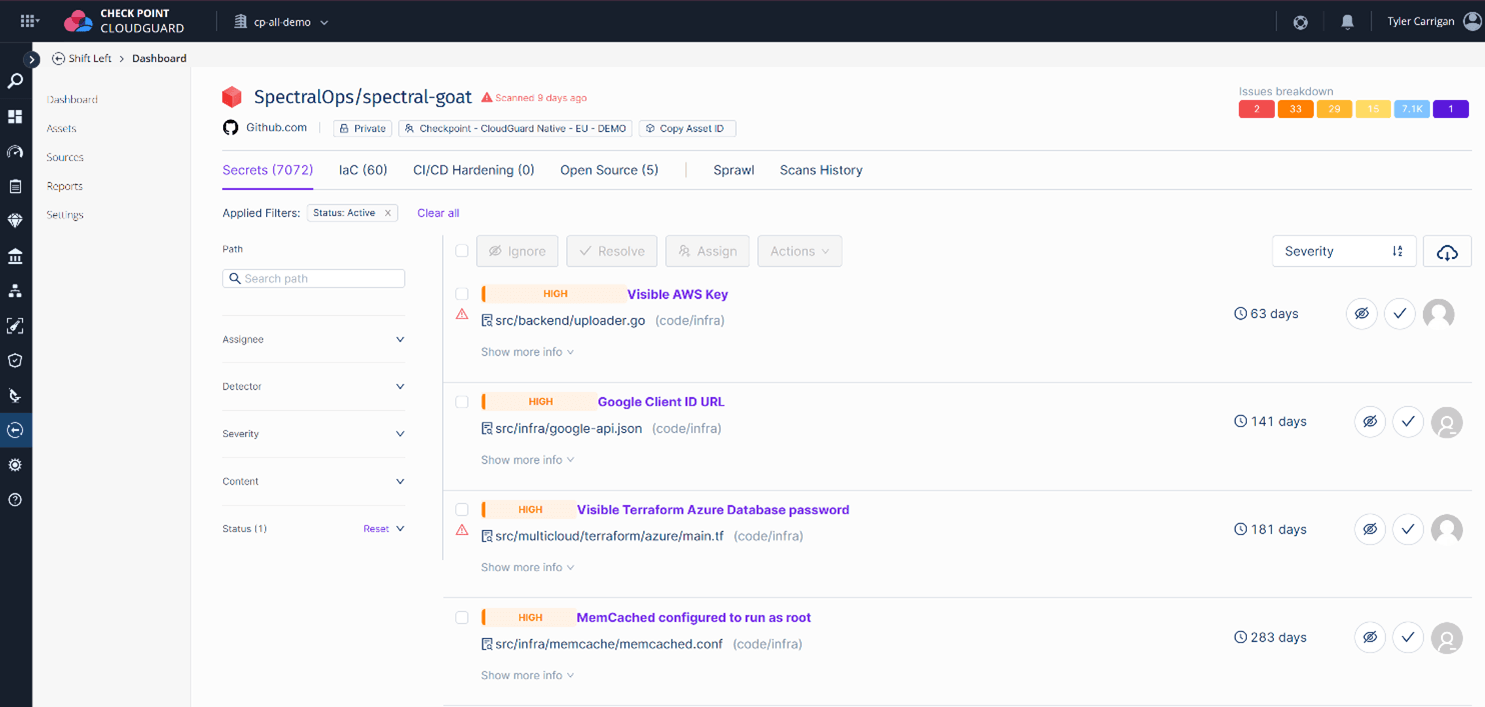
Secrets, such as API keys, passwords, or cryptographic keys, are often used to authenticate and authorize access to cloud resources. If these secrets are exposed in code and not properly protected, malicious actors can gain unauthorized access to sensitive cloud assets. Detecting secrets in code helps prevent unauthorized access, which aligns with the core Zero Trust principle of “never trust, always verify.”
With CloudGuard Code Security, organizations can detect secrets and misconfigurations in their code prior to deployment.
Identity Management
In today’s age of complex cloud infrastructure, managing user entitlements can be a daunting task for security teams. Manually assigning and revoking permissions for numerous actors and resources across multiple cloud infrastructures, each with their unique frameworks, is impractical and unscalable. Furthermore, the existence of multiple access permissions for a single entity adds to the complexity of accurately determining the correct permissions for each entity.
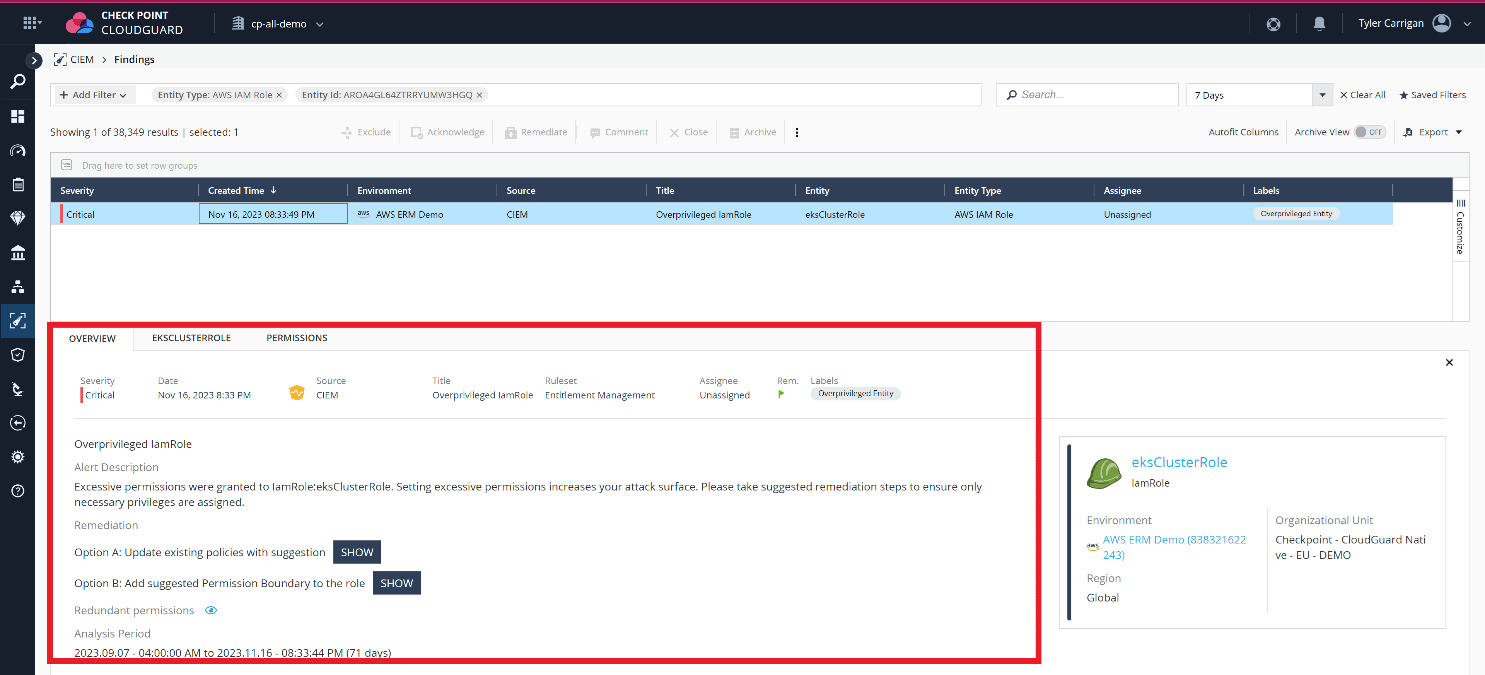
Through the utilization of CIEM solutions, security teams are empowered to efficiently oversee and regulate user identities and access to cloud-based resources and infrastructures. With the aid of CIEM solutions, the least-privileged access model can be established across all cloud environments, significantly mitigating the threat of cyber-attacks arising from overly permissive access permissions. This model ensures that identities are granted only the necessary permissions to execute their tasks, while also detecting and offering remediation suggestions for overly permissive entitlements.
CloudGuard CIEM creates effective user roles, which detect when there are conflicts between two organization-level rules and a third individual permission rule.
CIEM then analyzes the effective user roles and all cloud entitlements to accurately determine the permissions that entities receive within organizational environments.
CloudGuard CIEM continuously analyzes effective user permissions versus actual usage and offers remediation suggestions based on this analysis. By analyzing logs of a user’s activity in the last 90 days, it determines whether an organization has enforced the principle of least privilege. If an organization does not follow the principle of least privilege, a remediation action is created to suggest ways in which the user’s role can be optimized and enhanced. This ensures Zero Trust is enforced across all of your cloud environments.
With CloudGuard CIEM, organizations can effectively analyze their various cloud accounts, user groups, and entities, resulting in a highly secure environment. However, it is equally important for organizations to ensure the security of their keys and secrets.
Code Security
For optimal security measures, Zero Trust principles must be implemented in all areas of an organization. One crucial aspect is ensuring that code is thoroughly inspected for keys and secrets instead of anyone trusting that code is secured. This is where CloudGuard Spectral’s Secret Scanning comes in, effectively detecting hardcoded secrets, before deployment. By seamlessly integrating into the development lifecycle, Spectral can quickly scan code within seconds, providing developers with a frictionless experience as they incorporate it into their development process. Through the CloudGuard dashboard, an organization’s security team can monitor and supervise this process as well. Spectral’s lightweight and comprehensive approach to security ensures the protection of your codebase and enhances the organization’s overall Zero Trust framework.
Implement Zero Trust Security with Check Point CloudGuard
To truly embrace a ‘never trust, always verify’ approach, it is imperative to implement a least privilege framework across your cloud environments and prevent the exposure of keys and secrets within code. CloudGuard provides a unified platform to enforce these measures across security and development teams. It enables security teams to manage users and roles across multi-cloud as well as code security across the development lifecycle. It ensures continuous scanning and notifications on findings to the right developer within seconds, enabling both high standards of cloud security and an outstanding developer experience.
See Check Point CloudGuard’s Zero Trust Security in Action
Getting Started
For more information about building a Zero Trust strategy with Check Point CloudGuard, contact your Check Point account team or schedule a demo.









