
Average Weekly Global Cyberattacks peak with the highest number in 2 years, marking an 8% growth year over year, according to Check Point Research
Highlights
- Q2 2023 saw an 8% surge in global weekly cyberattacks, with organizations facing an average of 1258 attacks per week
- Education and Research experiencing highest number of attacks per week
- 1 out of every 44 organizations worldwide experience a Ransomware attack every week
- Africa & APAC face the highest YoY increase in weekly attacks per organization.
Never a dull moment when it comes to cyberattacks.
While the disruptive impact of the Russo-Ukrainian conflict on the cyber landscape has relatively reduced in recent months, the threat landscape has returned to a state of “normality.” This new normal is characterized by an increase in cyberattacks, as this report unravels the use of new evasive tactics, frequent hacktivism-based attacks, and a daily barrage of ransomware targeting numerous organizations. Despite the waning effect of the conflict on the cyber threat landscape, the persistence of these threats highlights the ongoing need for heightened vigilance and robust cybersecurity measures to counteract the relentless and evolving nature of cyberattacks.
In recent months, we have reported the unravelling of a Chinese-based APT which targeted governmental entities, hidden malware that was spotted behind legitimate looking apps, a new version of Chinese espionage that was propagated through USB devices and a malicious firmware implants discovered on internet routers. In addition, cybercriminals continue to leverage the latest AI revolution, by stretching the borders of generative AI chat platforms such as ChatGPT4.
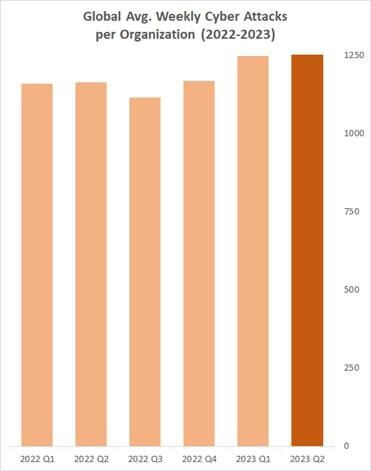
Overall Global Attacks – Highest number noted by Check Point Research in the past 2 years
In Q2 2023, there was an 8% increase in global average weekly attacks compared to the previous year.
The average number of attacks per organization per week reached 1258 attacks – the highest number noted by Check Point Research in the past 2 years.
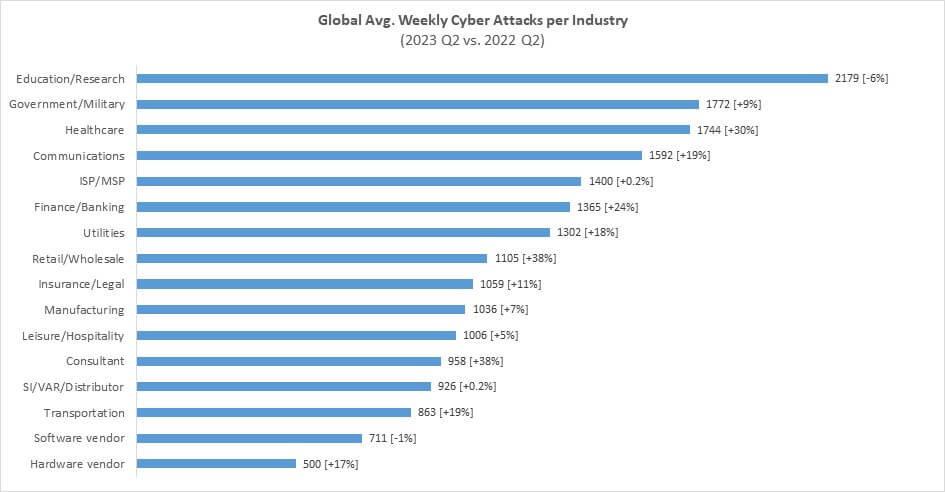
Attacks per Industry: Education / Research tops the list, Healthcare sees a significant rise in average weekly attacks
During Q2 2023, the Education/Research sector experienced the highest number of attacks, with an average of 2179 attacks per organization per week, marking a 6% decrease compared to Q2 2022. The Government/Military sector was the second most attacked, with an average of 1772 attacks per week, which represents a 9% increase from the parallel period last year. The Healthcare sector followed closely behind, with an average of 1744 attacks per week, reflecting a significant YoY increase of 30%.
Overall Attacks per Region: Africa & APAC top targeted regions
During Q2 2023, Africa experienced the highest average number of weekly cyber-attacks per organization, with an average of 2164 attacks. This signifies a significant year-on-year increase of 23% compared to the same period in 2022. The APAC region also witnessed a substantial 22% YoY increase in the average number of weekly attacks per organization, reaching an average of 2046 attacks.
|
Region |
Weekly Average of attacks per org |
YoY Change |
|
Africa |
2164 |
+23% |
| APAC |
2046 |
+22% |
| North America |
1011 |
+18% |
| Latin Americas |
1745 |
+9% |
| Europe |
1013 |
+5% |
Ransomware Attacks per Region:
In Q2 2023, 1 out of every 44 organizations worldwide experienced a ransomware attack, representing a decrease of 9% compared to Q2 2022, where 1 out of every 40 organizations suffered from such attacks. APAC & Europe sees significant Year Over Year increase in Ransomware attacks per organization, with a 29% and 21% increase respectively. The north American region follows with a 15% Year over year increase.
|
Region |
Organization Attacked Ratio (1:X) |
YoY Change |
| APAC |
1 out of 26 |
+29% |
| Europe |
1 out of 54 |
+21% |
| North America |
1 out of 94 |
+15% |
| Africa |
1 out of 30 |
-30% |
| Latin Americas |
1 out of 26 |
-12% |
Global Ransomware Attacks per Industry: Cybercriminals are after government & Military organizations
In Q2 2023, the Government/Military sector experienced the highest number of ransomware attacks, with 1 out of every 25 organizations impacted, marking a slight 4% decrease compared to the previous year. The Healthcare sector was the second most affected, with 1 out of every 27 organizations experiencing such attacks, representing an increase of 16% YoY. The Education/Research industry followed closely behind, with 1 out of every 31 organizations affected by ransomware, indicating a decrease of 2% over the past year.
| Industry | Organization Attacked Ratio (1:X) | YoY Change |
| Consultant | 1 out of 38 | 128% |
| Insurance/Legal | 1 out of 47 | 71% |
| Utilities | 1 out of 37 | 60% |
| Transportation | 1 out of 49 | 43% |
| Leisure/Hospitality | 1 out of 55 | 41% |
| Finance/Banking | 1 out of 31 | 33% |
| Communications | 1 out of 37 | 24% |
| Healthcare | 1 out of 27 | 16% |
| SI/VAR/Distributor | 1 out of 41 | 15% |
| Software vendor | 1 out of 65 | 13% |
| Hardware vendor | 1 out of 73 | 7% |
| ISP/MSP | 1 out of 36 | 2% |
| Manufacturing | 1 out of 48 | 0.30% |
| Education/Research | 1 out of 31 | -2% |
| Government/Military | 1 out of 25 | -4% |
| Retail/Wholesale | 1 out of 60 | -11% |
Cyber Safety Tips:
- Up-to-Date Patches: Keeping computers and servers up-to-date and applying security patches, especially those labeled as critical, can help to limit an organization’s vulnerability to cyberattacks
- Cyber Awareness Training: Frequent cybersecurity awareness training is crucial to protecting the organization against cyberattacks. This training should instruct employees to do the following:
- Not click on malicious links
- Never open unexpected or untrusted attachments
- Avoid revealing personal or sensitive data to phishers
- Verify software legitimacy before downloading it
- Never plug an unknown USB into their computer
- Strengthening User Authentication: Cybercriminals commonly use the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) and similar tools to gain remote access to an organization’s systems using guessed or stolen login credentials. Once inside, the attacker can drop ransomware on the machine and execute it, encrypting the files stored there. This potential attack vector can be closed through the use of strong user authentication. Enforcing a strong password policy, requiring the use of multi-factor authentication, and educating employees about phishing attacks designed to steal login credentials are all critical components of an organization’s cybersecurity strategy.
- Keep your software updated. Attackers sometimes find an entry point within your apps and software, noting vulnerabilities and capitalizing on them. Fortunately, some developers are actively searching for new vulnerabilities and patching them out. If you want to make use of these patches, you need to have a patch management strategy in place—and you need to make sure all your team members are constantly up to date with the latest versions.
- Choose Prevention over detection: Many claim that attacks will happen, and there is no way to avoid them, and therefore the only thing left to do is to invest in technologies that detect the attack once it has already breached the network and mitigate the damage as soon as possible. This is not true. Not only can attacks be blocked, but they can be prevented, including zero-day attacks and unknown malware. With the right technologies in place, most attacks, even the most advanced ones, can be prevented without disrupting the normal business flow.
- Anti-Ransomware Solutions: Some ransomware operators use well-researched and highly targeted spear phishing emails as their attack vector. These emails may trick even the most diligent employee, resulting in ransomware gaining access to an organization’s internal systems. Protecting against this ransomware that “slips through the cracks” requires a specialized security solution. To achieve its objective, ransomware must perform certain anomalous actions, such as opening and encrypting large numbers of files. Anti-ransomware solutions monitor programs running on a computer for suspicious behaviors commonly exhibited by ransomware, and if these behaviors are detected, the program can take action to stop encryption before further damage can be done.









